A Cardiac CT Scan (Computerized Tomography) is an advanced, non-invasive imaging technique that uses X-rays to create detailed, three-dimensional images of the heart and its blood vessels. This technology has revolutionized the way cardiovascular diseases are diagnosed, allowing doctors to see the heart’s structure and function with unparalleled clarity. It enables the detection of conditions such as coronary artery disease (CAD), blockages, and calcifications, which are major causes of heart attacks and other heart-related complications.
The procedure itself is relatively quick, typically taking less than 20 minutes, during which the patient lies on a bed that slides through a scanner. The machine takes multiple X-ray images from various angles, and a computer processes these to produce highly detailed cross-sectional images. A contrast dye is often used to enhance the clarity of the blood vessels, enabling accurate visualization of arteries, veins, and chambers of the heart.
The importance of Cardiac CT lies in its ability to detect heart disease in its early stages, often before symptoms manifest. Early detection is crucial because it provides the opportunity for preventive measures, lifestyle changes, or treatments that can drastically reduce the risk of life-threatening events like heart attacks. Unlike traditional angiography, which is invasive and requires inserting a catheter into the arteries, a Cardiac CT Scan is non-invasive and safer, providing a less risky alternative to diagnosing coronary artery problems.
In today’s healthcare landscape, where cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) are the leading cause of death globally, having access to advanced diagnostic tools like Cardiac CT Scans is essential. Early diagnosis through such imaging techniques is a key factor in reducing the mortality rates associated with heart diseases. This makes Cardiac CT Scans not just important but life-saving for high-risk individuals or those with a family history of cardiovascular diseases.
Understanding the Use and Awareness of Cardiac CT Scans in the World and India
This blog aims to provide an in-depth exploration of Cardiac CT Scans from both a global and an Indian perspective. While the use of this diagnostic technology is growing worldwide, the level of awareness, access, and adoption varies significantly between developed nations and developing countries like India.
On the global stage, Cardiac CT Scans are routinely used in many developed countries as part of comprehensive heart health screenings. In nations like the USA, UK, and many parts of Europe, these scans are integral to early diagnosis and prevention of heart diseases. People are more aware of the importance of preventive health measures, and healthcare systems are well-equipped with the necessary infrastructure to provide these services. Consequently, the routine use of Cardiac CT Scans has been shown to significantly reduce the rates of undiagnosed coronary artery disease and related deaths.
However, in India, the situation is notably different. India faces a dual challenge: a high burden of cardiovascular diseases and a relatively low level of awareness about preventive diagnostic techniques like Cardiac CT Scans. Despite cardiovascular diseases being a leading cause of death in the country, many Indians are either unaware of the benefits of Cardiac CT or lack access to such advanced medical technology. There are several reasons for this, including:
- Limited awareness: Preventive healthcare practices, including heart scans, are not widely promoted or understood by the general public in India. Many people are only introduced to these techniques after they show symptoms of heart disease, which may be too late.
- Access challenges: Cardiac CT Scans are primarily available in top-tier hospitals located in major urban centers. For the vast majority of India’s population, especially in rural areas, access to such advanced diagnostic tools is limited.
- Cost barriers: The cost of a Cardiac CT Scan is often prohibitive for many Indian families, as it is not always covered by basic health insurance plans. This financial burden discourages many from opting for preventive screenings.
2. Understanding Cardiac CT Scan
What is a Cardiac CT Scan?
A Cardiac CT Scan (Computerized Tomography) is a cutting-edge, non-invasive imaging procedure designed to capture highly detailed images of the heart and its associated blood vessels, particularly the coronary arteries. This scan allows doctors to visualize the internal structure of the heart without needing to perform invasive procedures, such as inserting catheters or performing surgeries. It is often used to diagnose various heart-related conditions, especially coronary artery disease (CAD), which occurs when the coronary arteries become narrowed or blocked due to plaque buildup.
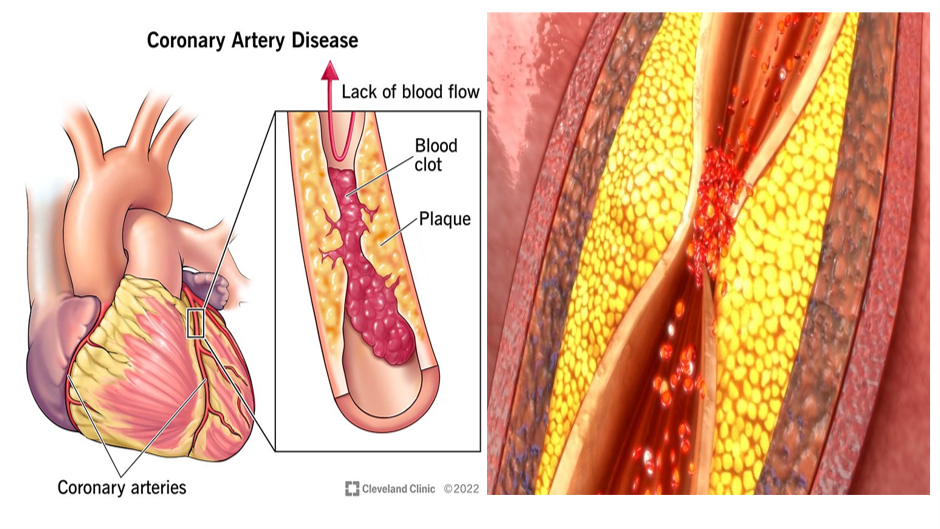
Coronary artery disease (CAD)
Basics of a Cardiac CT Scan
- Non-invasive: A key advantage of the Cardiac CT Scan is that it does not require any surgical intervention. The patient lies comfortably on a bed while a specialized machine uses X-rays to scan the heart.
- Detailed Imaging: The scan produces precise, cross-sectional images of the heart, providing a 3D view that shows the structure and functioning of the heart chambers, valves, and blood vessels. This detailed imagery helps physicians assess the health of the heart and detect abnormalities that may not be visible through other diagnostic methods like an electrocardiogram (ECG) or echocardiogram.
- Used to view coronary arteries and heart structures: Cardiac CT is particularly valuable in visualizing the coronary arteries, which supply oxygen-rich blood to the heart. This allows doctors to detect blockages, calcifications, or narrowing (stenosis) of these arteries that can lead to heart attacks or other severe cardiovascular events.
How It Works: Creating 3D Images Using X-rays
A Cardiac CT Scan involves the use of multiple X-rays taken from different angles around the body. These X-rays are then processed by a computer to construct highly detailed, three-dimensional images of the heart and its blood vessels. Here’s how the process works step-by-step:
- Preparation: The patient lies on a scanning table, and in some cases, a contrast dye is injected into the bloodstream. This dye helps highlight the blood vessels, making it easier to detect blockages or irregularities.
- Scanning Process: The scanning table moves through a doughnut-shaped machine called a CT scanner. Inside the scanner, an X-ray tube rotates around the patient’s body, emitting X-ray beams from multiple angles.
- Image Capture: As the X-ray beams pass through the heart, detectors on the opposite side of the machine record the amount of radiation absorbed by different tissues in the body. The denser tissues, like bones or calcified plaque, absorb more X-rays, whereas softer tissues, like the heart muscle or blood, absorb less.
- Image Construction: The data collected by the detectors is processed by a computer, which then generates a series of cross-sectional images, or “slices,” of the heart. These images can be combined to form a detailed 3D view, allowing the doctor to rotate and examine the heart from different angles.
- Radiation Exposure: While the procedure involves exposure to X-rays, modern machines are designed to minimize the radiation dose. Technological advancements have significantly reduced the amount of radiation used during scans, making the procedure safer for patients.
Role in Diagnosing Heart Diseases
The primary role of a Cardiac CT Scan is to assist in the early detection and diagnosis of various heart conditions, particularly coronary artery disease (CAD), which is one of the leading causes of death globally. Below are some of the key ways a Cardiac CT Scan is used in diagnosing heart diseases:
- Detection of Coronary Artery Disease (CAD):
- CAD occurs when plaque (a mixture of fat, cholesterol, and other substances) builds up inside the coronary arteries, leading to narrowing or blockages. This reduces blood flow to the heart muscle, potentially causing chest pain (angina) or a heart attack.
- A Cardiac CT Scan can detect calcified plaque in the coronary arteries (known as coronary artery calcification), even before symptoms of heart disease appear. This allows for early intervention, such as lifestyle changes or medication, to prevent the progression of the disease.
- Assessment of Blockages and Narrowing:
- The scan can measure the degree of stenosis (narrowing) in the arteries. If the arteries are significantly blocked, it may necessitate further interventions like angioplasty or surgery.
- In some cases, the scan may be part of a CT coronary angiography (CTA), where the focus is specifically on detecting any blockages in the coronary arteries.
- Evaluating Other Heart Structures:
- A Cardiac CT Scan can also provide detailed information about the heart’s chambers, valves, and muscle. It helps diagnose conditions like congenital heart defects, valvular heart disease, and pericardial diseases (issues with the lining around the heart).
- It is also useful in detecting tumors, blood clots, or aneurysms in the heart.
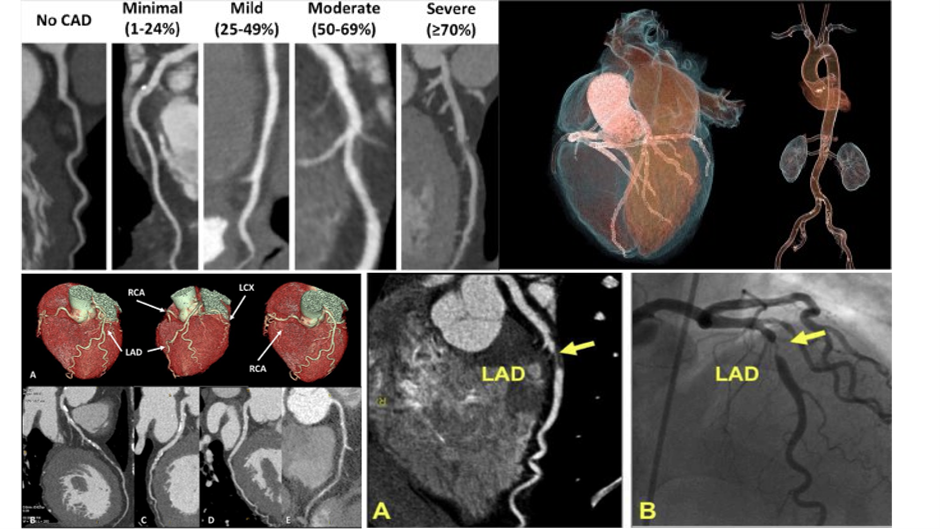
A comprehensive overview of the diagnostic capabilities of a Cardiac CT Scan in detecting and assessing Coronary Artery Disease (CAD). The scan reveals the buildup of plaque in coronary arteries, evaluates the degree of narrowing (stenosis)
- Pre-surgical Planning:
- In patients undergoing cardiac surgery, such as coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) or valve replacement, a Cardiac CT Scan can help surgeons plan the procedure by providing detailed images of the heart’s anatomy.
- Monitoring After Treatment:
- After procedures like stent placement or surgery, Cardiac CT can be used to monitor the patient’s progress and ensure that the heart and arteries are healing correctly without new blockages forming.
3. Global Perspective on Cardiac CT Scans
Adoption and Use Worldwide
Developed Nations: Routine Use in Cardiac Health Screening
In developed countries like the United States, United Kingdom, and across Europe, Cardiac CT Scans have become an integral part of cardiac healthcare. These countries have adopted this technology as a routine diagnostic tool for individuals at risk of cardiovascular diseases, especially those with symptoms of coronary artery disease (CAD) or who have risk factors such as high cholesterol, high blood pressure, smoking, diabetes, or a family history of heart disease.
In the USA, Cardiac CT Scans, especially CT coronary angiography (CTA), are frequently used in emergency rooms to quickly diagnose or rule out CAD in patients with chest pain. The American Heart Association (AHA) has endorsed the use of coronary CT angiography as part of the diagnostic pathway for intermediate-risk patients. Due to this widespread adoption, CT scans have become a primary tool for early detection and prevention of heart attacks and other cardiovascular events.
Similarly, in the United Kingdom, Cardiac CT is routinely offered in many National Health Service (NHS) hospitals as part of National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) guidelines. The scans are used both for diagnosing CAD and assessing the risk of future cardiovascular events, particularly in individuals who do not show severe symptoms but are at risk of heart disease. This helps in preventive treatment strategies, reducing the likelihood of emergency interventions later.
In Europe, countries such as Germany, France, and the Netherlands have also integrated Cardiac CT into routine diagnostic procedures. The European Society of Cardiology (ESC) supports the use of Cardiac CT for evaluating chest pain in patients where the risk of CAD is uncertain or for whom a more invasive procedure, like catheter angiography, is not immediately necessary.
Statistics on Cardiac CT Scan Adoption and Impact on Reducing Heart Disease Mortality Rates
The adoption of Cardiac CT Scans in these regions has had a significant impact on reducing heart disease mortality rates. The use of Cardiac CT is closely linked with the early detection of coronary artery disease (CAD), which remains the leading cause of death globally.
- United States:
- Studies in the USA have shown that the increased use of Cardiac CT has led to a 30-40% reduction in cardiac mortality in populations where it is widely used for preventive screening.
- According to research published by the American Journal of Cardiology, Cardiac CT scans have helped in reducing unnecessary invasive procedures like coronary catheterization by up to 70%. This not only reduces patient risk but also lowers healthcare costs significantly.
- Europe:
- In Germany, a study found that the use of Cardiac CT in coronary artery disease assessment reduced the need for invasive coronary angiography by 50% in patients at intermediate risk of heart disease.
- Another European multi-center study found that Cardiac CT Scan use in patients with suspected CAD resulted in better risk stratification, leading to more targeted treatments, which contributed to a reduction in major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE).
- United Kingdom:
- The UK’s NHS has implemented widespread Cardiac CT usage for individuals with suspected heart disease, reducing cardiac-related deaths by 20% over a ten-year period. Studies also show a 25% reduction in hospitalization rates for chest pain due to earlier, accurate diagnoses of heart disease using CT technology.
These statistics reflect the major role Cardiac CT Scans play in reducing heart disease mortality by facilitating early detection and appropriate interventions.
Examples of Advancements in CT Scan Technology
In recent years, significant technological advancements have made Cardiac CT Scans even more effective and safer, leading to their wider adoption worldwide. Below are some notable improvements:
1. Lower Radiation Doses
Historically, one of the concerns with CT scans, including Cardiac CT, was the exposure to high levels of radiation. However, advancements in technology have greatly reduced this risk. Modern Cardiac CT scanners now come equipped with dose reduction techniques, including:
- Iterative Reconstruction Algorithms: These advanced algorithms process the X-ray data more efficiently, producing clear images while using significantly less radiation. This can reduce the radiation dose by up to 50-80% compared to older models.
- Prospective ECG-gated Scanning: This method times the X-ray pulses with the patient’s heartbeat, so images are captured only during specific phases of the cardiac cycle, minimizing unnecessary radiation exposure.
These innovations have lowered the risk of radiation-induced complications, making Cardiac CT Scans a much safer option for regular screening, even for at-risk populations.
2. Higher Image Quality
Another key advancement is in the image resolution and the ability to visualize even the smallest details of the coronary arteries and heart structures. Newer CT machines, such as dual-source CT scanners and 64-slice or 128-slice scanners, can capture extremely fine details that were previously unattainable. This improved imaging quality allows for:
- Better visualization of coronary artery plaques: These high-resolution images make it easier to distinguish between soft (unstable) and calcified (stable) plaque, which is crucial for determining the risk of heart attack or stroke.
- Faster Scanning Times: The latest CT scanners are incredibly fast, capable of capturing detailed images in less than a second. This is particularly beneficial for patients who struggle to hold their breath for long periods or have irregular heart rhythms. For example, dual-source CT scanners can image the entire heart in just 250 milliseconds, even if the heart rate is above normal.
3. Functional Imaging and AI Integration
Recent advances in Artificial Intelligence (AI) and machine learning have also begun to enhance Cardiac CT by improving image analysis. AI algorithms are now being integrated into CT imaging systems to:
- Automatically identify areas of concern: AI-powered CT systems can detect and quantify coronary artery calcifications, helping radiologists identify blockages more efficiently.
- Predict future heart events: AI tools are being developed to analyze cardiac CT data and predict a patient’s risk of future cardiovascular events based on subtle markers that might not be immediately visible to the human eye.
Moreover, the incorporation of functional imaging into Cardiac CT—such as CT-based Fractional Flow Reserve (FFR)—is emerging as a major advancement. FFR-CT can measure the blood flow in coronary arteries, helping doctors determine if a blockage is significant enough to require treatment like angioplasty or stenting. This non-invasive alternative to traditional FFR can guide treatment decisions more effectively.
4. The Indian Perspective
Current State of Healthcare in India
The High Burden of Cardiovascular Diseases (CVDs) in India
India is facing a severe cardiovascular disease (CVD) epidemic, with heart diseases being one of the leading causes of death in the country. According to the Global Burden of Disease (GBD) study, cardiovascular diseases account for 28% of all deaths in India, making them the number one cause of mortality. Moreover, the Indian population tends to develop CVDs at a younger age compared to Western countries, with many cases occurring in individuals below the age of 50. This trend is alarming and calls for effective prevention, early diagnosis, and treatment strategies.

The rapid urbanization, changing lifestyles, increasing prevalence of risk factors such as hypertension, diabetes, smoking, and sedentary lifestyles, along with genetic predispositions, have contributed to the rising burden of heart disease in the country. Early diagnosis and intervention are crucial in preventing heart attacks, strokes, and other fatal complications of CVD, which is where Cardiac CT Scans can play a pivotal role.
How Often Cardiac CT Scans Are Used in Indian Hospitals
Despite the rising burden of cardiovascular diseases, Cardiac CT Scans are underutilized in India. Their use remains limited, with the majority of Indian hospitals relying on more traditional diagnostic methods such as electrocardiograms (ECG), stress tests, and echocardiography to assess heart health.
- Electrocardiograms (ECG) are widely available in almost all hospitals and clinics, and they are typically the first test conducted to check for any irregularities in heart rhythms or potential damage to the heart muscles.
- Echocardiography is another common diagnostic tool in India, used to visualize the heart’s movement and function using ultrasound waves. It helps in assessing heart chambers and valves but is limited in its ability to detect coronary artery blockages or plaque buildup.
In contrast, Cardiac CT Scans, which provide a detailed 3D view of the coronary arteries, are used less frequently. This is mainly because these scans are expensive, require specialized equipment and expertise, and are available only in larger cities or in high-end hospitals.
According to recent estimates, only a small percentage of hospitals, particularly tertiary care centers in metropolitan areas like Delhi, Mumbai, Bangalore, and Chennai, are equipped with the technology and expertise to perform Cardiac CT Scans. The lack of widespread availability of these advanced diagnostic tools has hindered their adoption, particularly in smaller towns and rural areas, where the majority of the population lives.
Comparison with Other Diagnostic Techniques
While Cardiac CT Scans offer superior imaging and are invaluable for detecting coronary artery disease (CAD), they are not as commonly used in India as ECG and echocardiography. Here’s a comparison of the three techniques:
- ECG (Electrocardiogram):
- Widely available and inexpensive.
- Used to detect heart rhythm abnormalities and signs of heart attacks.
- However, it cannot provide detailed images of coronary arteries or identify plaque buildup.
- Echocardiography:
- Non-invasive, safe, and widely available in both urban and semi-urban hospitals.
- Provides real-time images of the heart’s movement, chambers, and valves.
- Cannot assess coronary artery blockages or calcifications as effectively as Cardiac CT.

- Cardiac CT Scan:
- Provides highly detailed, 3D images of coronary arteries and the heart, allowing for the detection of CAD and plaque buildup.
- Far superior for early detection of coronary artery disease compared to ECG or echocardiography.
- Limited in availability and expensive, which restricts its routine use in many parts of India.
Challenges in Adoption
1. Lack of Awareness Among Patients
One of the major barriers to the adoption of Cardiac CT Scans in India is the lack of awareness among the general population about the availability and benefits of this diagnostic tool.
- Many patients are unaware that Cardiac CT exists as a non-invasive method for detecting coronary artery disease.
- Indian patients often only seek medical help when symptoms like chest pain or shortness of breath become severe, at which point traditional methods like ECG or angiography are used.
- There is also limited public understanding of the importance of preventive health measures, including screening for heart disease in asymptomatic individuals. Unlike in Western countries, where preventive screenings are a part of routine healthcare, many Indians still do not undergo regular heart check-ups unless they have noticeable symptoms.
This lack of awareness is exacerbated by the limited outreach efforts by healthcare providers and the government, which could play a significant role in educating people about the advantages of early diagnosis through Cardiac CT Scans.
2. Limited Access
Another significant challenge is the limited access to Cardiac CT Scan technology, which is primarily concentrated in urban centers.
- Urban vs. Rural Divide: Most advanced diagnostic centers offering Cardiac CT are located in metropolitan cities such as Delhi, Mumbai, Bangalore, and Chennai. In contrast, rural areas, where 70% of India’s population resides, have very limited access to such high-end diagnostic tools.
- Availability in Specialized Hospitals: Even in urban centers, not all hospitals offer Cardiac CT Scans. Only tertiary care hospitals or private facilities equipped with modern infrastructure tend to offer this service, further limiting its availability to the general population.
This urban-rural divide in healthcare infrastructure means that a vast majority of the population in India does not have easy access to Cardiac CT Scans, making it challenging for individuals, especially those in remote regions, to benefit from this technology.
3. Cost Barriers
The high cost of Cardiac CT Scans is another major obstacle to their widespread use in India. The price for a Cardiac CT Scan in India can range from ₹10,000 to ₹20,000 ($125 to $250), depending on the hospital and the city. This is a significant expense for a large portion of the population, especially in a country where the per capita income remains relatively low.
- Insurance Coverage: While some private insurance plans may cover the cost of a Cardiac CT Scan, many government insurance schemes or low-cost health insurance plans do not. This lack of coverage makes it difficult for lower- and middle-income families to afford this advanced diagnostic procedure.
- Alternative Methods: Due to the cost, many patients and healthcare providers opt for less expensive methods like ECG or stress tests, even though these may not provide the same level of detail as a Cardiac CT Scan.
The high cost of Cardiac CT Scans limits their use, particularly among lower-income groups and in government-run hospitals, where resources are stretched thin.
4. Healthcare Infrastructure Gaps
India faces significant healthcare infrastructure gaps, particularly when it comes to providing advanced diagnostic tools like Cardiac CT Scans across the country. These gaps are especially pronounced in smaller towns and rural areas, where:
- Lack of Specialized Centers: Advanced diagnostic centers equipped with Cardiac CT Scanners are few and far between, limiting access to preventive cardiac care.
- Shortage of Trained Technicians: Operating a Cardiac CT Scanner requires specialized training. The shortage of skilled radiologists and technicians who can perform and interpret these scans further hampers their use in smaller healthcare facilities.
- Inconsistent Quality of Care: The quality of cardiac care varies significantly between urban tertiary care hospitals and smaller healthcare facilities, meaning that even where Cardiac CT Scanners are available, patients may not receive the same standard of care.
Addressing these infrastructure gaps is essential to improving access to Cardiac CT Scans and ensuring that patients in smaller towns and rural areas can benefit from this life-saving technology.
6. Advantages of Cardiac CT Scans
1. Early Detection of Heart Disease
One of the most significant advantages of a Cardiac CT Scan is its ability to detect heart disease early, often before symptoms appear. This early detection is crucial in preventing the progression of serious conditions such as coronary artery disease (CAD), which is the most common form of heart disease and a leading cause of heart attacks.
- Detection of Coronary Artery Disease (CAD): A Cardiac CT Scan can identify calcified plaque buildup in the coronary arteries, which can restrict blood flow to the heart. By diagnosing CAD in its early stages, doctors can intervene before the condition becomes severe enough to cause chest pain (angina), shortness of breath, or heart attacks.
- Risk Stratification: Cardiac CT Scans allow doctors to assess a patient’s heart disease risk more accurately. Based on the scan results, healthcare providers can recommend preventive strategies, such as lifestyle changes, medication, or closer monitoring, to reduce the risk of future heart-related complications.
- Pre-symptomatic Diagnosis: The ability to detect heart disease before any symptoms occur is particularly beneficial for individuals with risk factors like high blood pressure, high cholesterol, diabetes, or a family history of heart disease. These individuals may appear healthy on the surface but could have underlying heart conditions that a Cardiac CT Scan can uncover early on, allowing for timely interventions.
2. Non-invasive and Safe
Another major benefit of Cardiac CT Scans is that they are non-invasive, making them a safer alternative to traditional coronary angiography.
- Non-invasive Procedure: Unlike traditional angiography, which requires the insertion of a catheter into a blood vessel to assess the coronary arteries, a Cardiac CT Scan does not involve any surgical procedures. The patient lies on a table while the scanner takes detailed images of the heart, making it a far less invasive and more comfortable experience.
- Minimal Risk: Because it is a non-invasive procedure, a Cardiac CT Scan carries minimal risk compared to invasive tests. There is no need for hospital stays or recovery time, and patients are typically able to return to their normal activities immediately after the scan.
- Safe and Reliable: Modern Cardiac CT machines use lower radiation doses due to advancements in CT technology, which have significantly reduced the amount of radiation exposure during the scan. This makes the procedure safer for a wider range of patients, including those who may need multiple scans over time to monitor their heart health.
- Contrast Dye Use: In some cases, a contrast dye is used during the scan to enhance the visibility of blood vessels. Although there is a small risk of allergic reactions to the dye, it is generally well-tolerated by most patients, and the procedure is considered very safe overall.
3. Better Outcomes
The early detection provided by Cardiac CT Scans leads to better patient outcomes, as it allows for timely interventions and lifestyle changes that can prevent heart disease from worsening.
- Preventive Treatments: For individuals with early signs of coronary artery disease, timely diagnosis through a Cardiac CT Scan can result in preventive treatments that significantly reduce the risk of heart attacks or other cardiovascular events. Treatments may include cholesterol-lowering medications, blood pressure management, or aspirin therapy to reduce blood clot risks.
- Lifestyle Modifications: A clear diagnosis often motivates patients to make necessary lifestyle changes, such as improving their diet, exercising more, quitting smoking, or managing stress. These changes can have a profound impact on heart health, potentially reversing early-stage coronary artery disease and preventing future complications.
- Reduced Hospitalizations and Emergencies: Early detection means that interventions can be done in a more controlled, non-emergency setting, reducing the risk of sudden heart attacks and the need for emergency treatments. This can also lead to fewer hospitalizations, improving quality of life and reducing healthcare costs for both patients and the healthcare system.
- Informed Decision-Making: The detailed images provided by a Cardiac CT Scan help doctors and patients make more informed decisions regarding treatments. Whether it’s medication, lifestyle changes, or even more invasive procedures like stenting or bypass surgery, having a clearer picture of the heart’s condition enables healthcare providers to tailor treatment plans specifically to the patient’s needs, improving long-term outcomes.
7. Recommendations for Increasing Awareness in India
1. Public Awareness Campaigns
One of the most effective ways to increase the adoption of Cardiac CT Scans in India is through comprehensive public awareness campaigns. Many people in India remain unaware of the importance of preventive heart care and the role that advanced diagnostics like Cardiac CT Scans can play in early detection and prevention of heart diseases.
- Educational Initiatives: Healthcare organizations, hospitals, and the Indian government should collaborate on educational campaigns aimed at increasing awareness about the dangers of cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) and the importance of early diagnosis. These campaigns can include public service announcements, seminars, health camps, and online platforms where people are educated on heart health.
- Mass Media Outreach: Leveraging mass media such as television, radio, newspapers, and social media can significantly boost awareness about Cardiac CT Scans. Targeted campaigns using popular social media platforms like YouTube, Facebook, and Instagram could reach millions, particularly younger demographics and those with a family history of heart disease.
- Focus on Prevention: Messaging should highlight how Cardiac CT Scans can detect coronary artery disease even before symptoms appear, reducing the risk of sudden heart attacks and other life-threatening conditions. Emphasizing the role of preventive diagnostics as a part of routine healthcare can change the prevailing attitude that healthcare is only necessary when symptoms are severe.
2. Inclusion in Routine Health Check-ups
To encourage the use of Cardiac CT Scans, it is essential to include them as a part of routine heart health assessments, especially for individuals at high risk of cardiovascular diseases. Many people in India only undergo basic health check-ups like blood pressure monitoring, ECG, or blood tests, but these tests may not be sufficient to detect coronary artery disease early.
- Routine Screening for High-Risk Individuals: Cardiac CT Scans should be recommended as part of routine check-ups for individuals who have known risk factors such as hypertension, diabetes, high cholesterol, obesity, smoking, or a family history of heart disease. These individuals are more prone to developing cardiovascular diseases at a younger age, and early detection through Cardiac CT can prevent future complications.
- Corporate Health Programs: Encouraging companies and businesses to incorporate Cardiac CT Scans into their employee health programs can also play a vital role. Large corporations often conduct annual health check-ups for their employees; adding Cardiac CT Scans to these screenings, particularly for high-risk groups, can help detect heart problems early, reduce absenteeism, and improve employee well-being.
- Promoting Screening in Healthcare Settings: Hospitals and clinics should promote Cardiac CT as a standard part of cardiovascular screenings alongside traditional tests like ECG and echocardiograms. Physicians should educate their patients about the benefits of Cardiac CT Scans and advise them to undergo the scan if they fall within the high-risk category.
3. Government Subsidies and Insurance Coverage
The high cost of Cardiac CT Scans in India presents a significant barrier to their widespread use. Addressing the cost issue is crucial to making these scans more accessible to the broader population, particularly lower- and middle-income families.
- Government Support: The Indian government can play a key role by providing subsidies or incentives to hospitals and diagnostic centers offering Cardiac CT Scans. This could lower the cost for patients, making the procedure more affordable for the general public.
- Insurance Coverage: Currently, many basic health insurance plans in India do not cover the cost of Cardiac CT Scans, forcing patients to pay out of pocket. The government, along with private insurance companies, should work on including Cardiac CT Scans in insurance plans, particularly for individuals with risk factors for cardiovascular disease. Ayushman Bharat, India’s flagship healthcare program, could also incorporate these scans into its coverage for heart disease screening and treatment.
- Subsidized Scans in Government Hospitals: Government-run hospitals, especially in smaller towns and cities, should be equipped with Cardiac CT scanners, and the cost of the scan should be subsidized for patients from economically weaker sections. This would increase access to advanced cardiac care for a larger segment of the population.
4. Collaboration Between Hospitals and Technology Firms
To expand access to Cardiac CT Scans and make them more widely available across India, collaborations between hospitals and technology firms are essential. Technology firms that specialize in diagnostic equipment can play a vital role in bridging the gap between availability and accessibility.
- Technological Partnerships: Public-private partnerships (PPP) between the government, private hospitals, and technology firms can help scale the availability of Cardiac CT Scans in both urban and rural areas. These partnerships can facilitate affordable leasing or purchase agreements for advanced scanning equipment, reducing upfront costs for hospitals and clinics.
- Mobile Diagnostic Centers: One innovative approach could be the development of mobile diagnostic centers equipped with Cardiac CT scanners that travel to underserved rural and semi-urban areas. Such mobile units, supported by government or private initiatives, could provide diagnostic services in regions where access to hospitals with advanced diagnostic tools is limited.
- Training Programs: Collaborating with technology firms to train healthcare workers and technicians in operating Cardiac CT scanners is crucial. Investment in specialized training programs can ensure that more hospitals are equipped with the expertise needed to run these scans, making them more accessible to patients.
- AI Integration: Technology firms specializing in Artificial Intelligence (AI) can further improve the accuracy and efficiency of Cardiac CT Scans by integrating AI-powered algorithms to assist in the interpretation of scan results. AI can help radiologists identify early-stage plaque buildup, enhance diagnostic accuracy, and potentially reduce the need for repeat scans, lowering costs for patients.
8. Conclusion
Global and Indian Outlook
Globally, Cardiac CT Scans have become a cornerstone of modern cardiology, widely used in developed nations such as the United States, United Kingdom, and Europe for early detection and prevention of heart diseases, especially coronary artery disease (CAD). The routine use of these scans in cardiac health screenings has significantly contributed to better health outcomes and reduced mortality rates from cardiovascular diseases in these regions. Advancements in technology, including lower radiation doses and improved image quality, have made Cardiac CT Scans safer, more accessible, and more effective in diagnosing heart diseases at early stages, leading to more timely interventions and better patient outcomes.
However, in India, the adoption of Cardiac CT Scans remains limited due to several challenges, including lack of awareness, limited access, and high costs. While the burden of cardiovascular diseases in India is among the highest in the world, Cardiac CT Scans are still underutilized, especially in rural and semi-urban areas. Many Indian patients are either unaware of the benefits of this advanced diagnostic tool or face financial barriers that prevent them from accessing it. Moreover, the concentration of Cardiac CT facilities in urban centers further exacerbates the problem, leaving a large portion of the population underserved.